Leveraging customer segmentation strategies leads to about 15% higher open rates and a 101% increase in clicks compared to non-segmented campaigns. Also, running campaigns without segmentation will prevent you from capitalizing on the power of hyper personalization. You must consider the unique needs, expectations, pain points, behavior, psyche, and more of different customer segments while communicating with them to maintain and nurture strong customer relationships.
Maintaining unique communication lines for all your customers will require you to segment them, but did you know there are many ways to segment the customers? Let’s learn more about different customer segmentation models and see six examples.
What is customer segmentation ?
Customer segmentation is the process of dividing customers into different segments based on similar parameters such as personality, interests, values, education, and demographics. Segmentation divides your customers into groups with similar needs and helps you efficiently personalize your communication and marketing efforts to meet your customers’ unique needs and expectations. This leads to high conversions and loyalty.
Why should you segment customers with multiple filters ?
Customer needs and psyche vary vastly even in the same segment—similar age or geographical cohorts. Therefore, using one or two segmentation filters on your entire user base will not make your campaigns very targeted to achieve significant sales. You need multiple layers of segmentation filters to establish personalized customer relationships and utilize the full potential of your marketing efforts.

There is no denying that creating a precise micro-segmentation strategy requires significant resources and would be difficult without a robust segmentation engine.
What are the types of customer segmentation models?
Here are eight segmentation models to make your campaigns highly targeted.
1. Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation divides the user base and the target market on demographic variables like gender, age, occupation, education, and income. Because it segments customers into broader categories, it is a great model for showcasing your products to the masses.
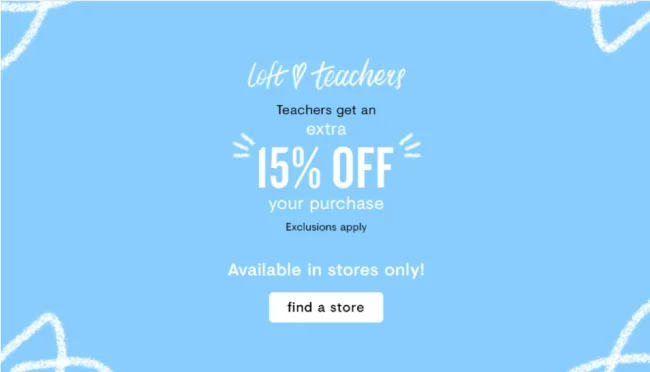
For example, LOFT, an ecommerce fashion brand, leveraged demographic segmentation to deliver hyper-targeted campaigns to users pursuing a specific occupation—teaching.
However, demographics give you a highly restricted view since individuals of a similar age or income group don’t necessarily have the same needs or mentality.
2. Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation segments your target audience based on their location or work in a country, region, city, or postal code. Location, population density, climate, culture, language, and time zone are the significant segments you can create with geographic segmentation.

Nike, for example, used the cultural reference factor of geographical segmentation in its Bleed Blue campaign to target a specific country: India. The campaign encouraged cricket enthusiasts to create blue digital handprints through Facebook and Nike’s official website. It used them as a symbol to support the Indian cricket team, which also won the World Cup after 28 years.
Geographical segmentation can also help you with ecommerce localization—translating your website and product information to the country’s language, using the correct currency, and leveraging cultural references in campaigns to make them more relevant.
Geographical segmentation is more straightforward as it requires fewer data points. However, users of the exact location can differ vastly in needs, psychology, expectations, etc.
3. Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation groups customers based on psychological characteristics—personality, lifestyle, social status, activities, interests, opinions, and attitudes.
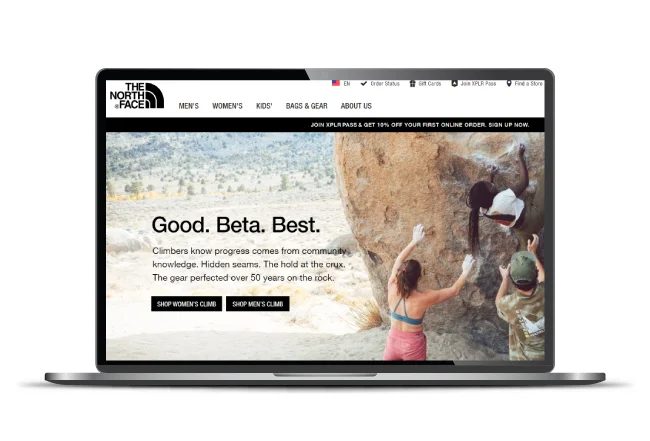
For example, the activewear and outdoor sports brand North Face uses lifestyle segments such as traveler, explorer, and hiker to target users with relevant products. The brand targets a specific lifestyle segment–climbers to deliver targeted messaging.
Organizations can access psychographic information by tracking users’ activity on social media platforms, websites, applications, and search engines and conducting market research and surveys. User patterns like time spent on websites, reviews posted, locations visited, payments done, and more add to it.
Psychographic segmentation helps you understand the customer’s journey and the reason behind their behavior and devise strategies, experiences, and products accordingly. It is more effective than geographical and demographic segmentation because it targets dynamic data but must be combined with other models for a more well-rounded and targeted approach.
4. Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation separates customers based on their behavior with your website or app—products viewed, clicked, added to cart, exited, and overall interaction with the brand on other platforms.
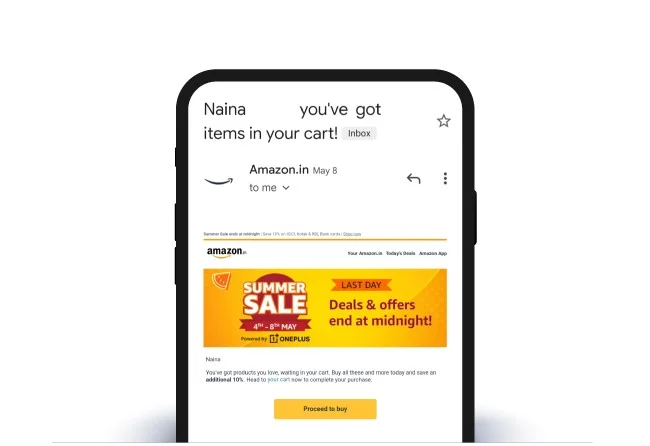
By tracking customers’ behavior with the brand and segmenting accordingly, Amazon targets customers who have abandoned their cart and incentivizes them to complete the purchase by reminding them of the ongoing sales and discount offers.
The most significant differentiator of behavioral segmentation is that it doesn’t rely on static data, like demographics or geography. It accurately targets the ever-changing buying behavior, which is why campaigns based on this can be more precise, personalized, and effective. Behavioral segmentation also drives unprecedented brand loyalty, puts you way ahead of the competition with targeted messaging, and helps reduce customer churn.
5. Technographic segmentation
Technographic segmentation divides customers based on the device (mobile or desktop), apps, or software they use.
H&M, for example, understands where its customers are coming from—desktop, tablet, or mobile, and optimizes its website accordingly.
You can even go a step further, identify which device they use, and personalize your marketing accordingly. This is important because Apple users were found to be the most valuable online shoppers when segmented by AOV and device.
Additionally, you can send personalized recommendations based on the customer’s device. For example, you can recommend external keyboards and mics to users who have purchased gaming laptops but haven’t purchased accessories.
6. Need-based segmentation
Need-based segmentation divides the customers based on a common problem they want to solve, a shared need, or specific must-haves they seek in a product.
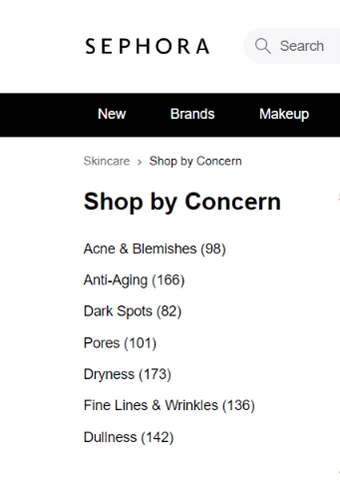
Sephora’s “Shop By Concern” category utilizes need-based segmentation to help customers filter products based on their problems and the benefits they seek.
The idea behind need-based segmentation is that understanding the user’s pain points will enable you to reach them with targeted recommendations.
There are two approaches to need-based segmentation—descriptive-first and needs-first. In descriptive-first, you start by using descriptive data (like demographics) to group customers and then identify the needs of each group. While in needs-first, you identify the needs of your audience first and then find how the descriptive data is related to each need.
7. Value-based segmentation
Value-based segmentation groups customers based on the economic value they generate for the business.
Apple, for example, releases smartphone models in different price segments to target different audiences based on how much they would spend and recommends upsells accordingly. Like watch SE to SE phone users, the premium watch 7 to iPhone 13 pro users, regular AirPods to mid-segment, and AirPods pro to high-value segment.

Value-based segmentation helps you identify your most and least profitable customer segments. This allows you to personalize your marketing efforts and optimize your budgets accordingly. Leveraging your best customers will always prove beneficial.
8. RFM-based segmentation
RFM segmentation groups customers based on recency, frequency, and monetary value. How recently did the customer interact with the brand or make a purchase, how frequently do they interact or purchase, and how much economic value did they generate for the brand.
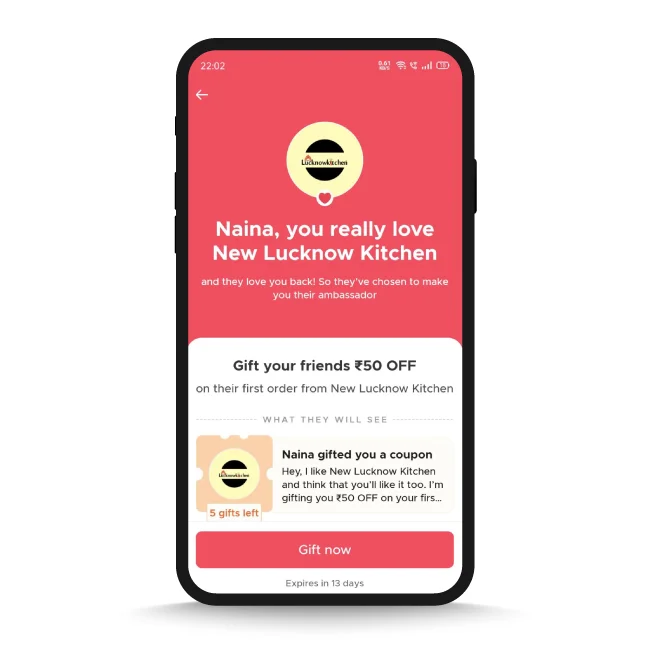
Zomato, for example, leverages RFM segmentation to identify groups of customers who frequently interact with and purchase from a particular restaurant, have done so recently, and thereby add high monetary value. Zomato rewards their loyalty by making them brand ambassadors for those restaurants.
Segregating customers based on their RFM scores will help you treat low-RFM and high-RFM customers differently. For example, you can reward customers with high RFM for their loyalty and continuous engagement with your brand and incentivize customers with low RFM to increase their interaction.
Like need-based and value-based segmentation, the RFM model works best with other segmentation filters, such as psychographic and behavioral segmentation.
9. Bonus: Predictive segmentation
The above segmentation methods are based on customers’ historical behavior with your brand. Predictive segmentation is a step further. It understands customers’ previous interactions and uses artificial intelligence to predict what the customer will do next. Based on these predictions, automatic triggers can display messages or offers while the customer is on the site or app. As a result, predictive segmentation helps change the customer’s future behavior.
For example, if a visitor’s actions display behavior indicative of them leaving the website, then predictive segmentation can be set to show appropriate messages to stop that.
6 Examples of customer segmentation
Let’s look at six examples of utilizing customer segmentation.
1. Activating new users
You can use customer segmentation to divide users into those who have launched your mobile application for the first time or have never launched it after downloading. You need to dedicate marketing efforts to activate these user segments.
Use channels such as emails, push notifications, and SMS to encourage new users to launch the app, take action, and return to your app.
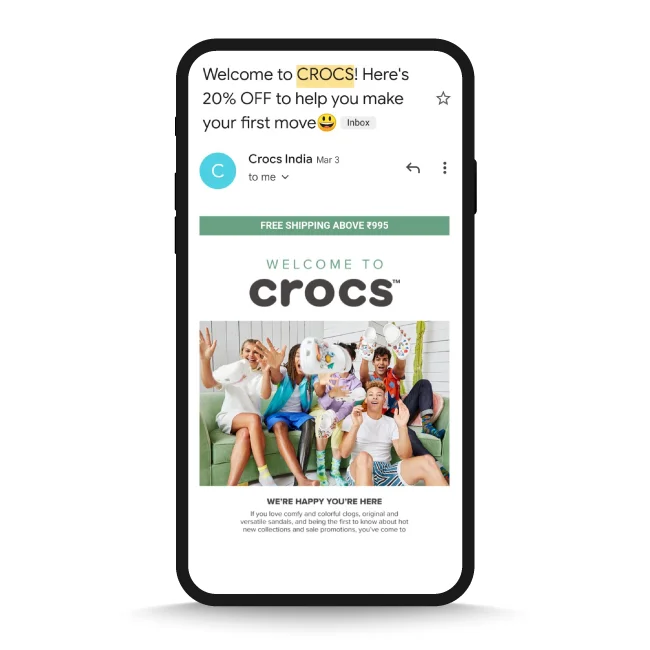
For example, Crocs has sent a welcome email to its new users who have downloaded the app and launched it for the first item. A discount incentivizes the users to make their first purchase or at least browse the app.
Using contextual nudges and walkthroughs also activates new users faster. It guides them to your app’s critical action without any delay, highlights the key features, and highlights relevant app elements.
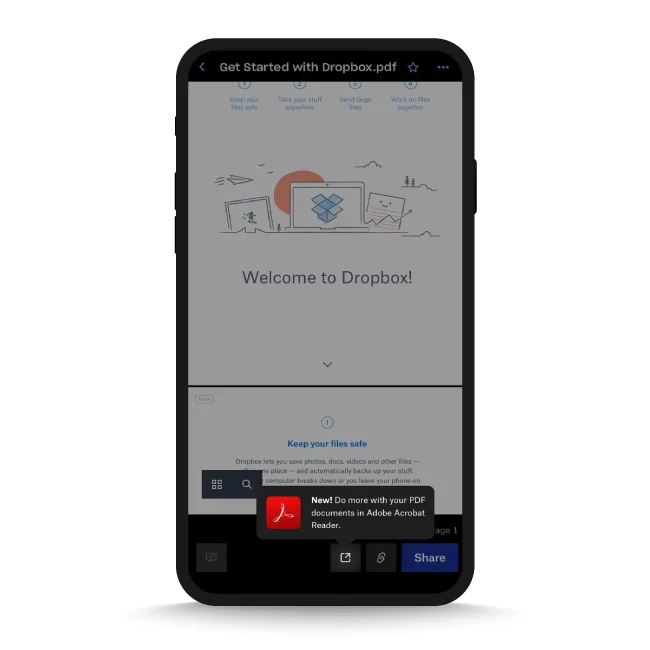
Here, for example, Dropbox activates new users by nudging them to perform more actions with a file, thereby increasing engagement.
2. Monetizing active users who have never purchased
You can use customer segmentation to identify active users who have yet to make their first purchase. Active users regularly launch your app at a frequency specific to your app. Because they are active users, you must have their behavioral history. Leverage that to send them personalized product recommendations, identify their friction points, and encourage them to purchase by offering discounts and offers.

For example, Jack & Jones has sent an email to its active users (who signed up but never made a purchase), encouraging them to buy what interests them. An RFM analysis helps identify opportunities for doing this.
3. Engage one-time purchasers
Using customer segmentation, segment users who have launched your app recently but don’t do it regularly. Getting a few one-off customer purchases is not sustainable in the long run. You need repeat customers who regularly buy from you. To engage them long-term, you must build your user’s habit loop around your app.
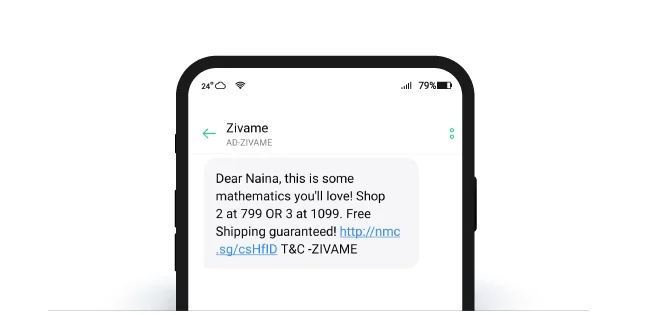
For example, Zivame engages a one-time purchaser via SMS, offering discounts, free shipping, and a deep link to take the user to a specific page.
Send push notifications, emails, and SMS with carefully curated content to keep engaging your customers. Make sure these SMS and notifications take them to their page of interest. Also, ensure that these users know, understand, and utilize features critical to their habit loop to become regular users. You can use nudges to highlight these features.
4. Re-engage users dormant from the last 90 days
This targets frequent users on your app who recently dropped off. You can create a segment of these users based on their recency and reduced frequency. To re-engage these users, send contextual and personalized push notifications or emails, update them on what’s new, and offer discounts to encourage them to purchase again. You need to define the value you wish to deliver to them.
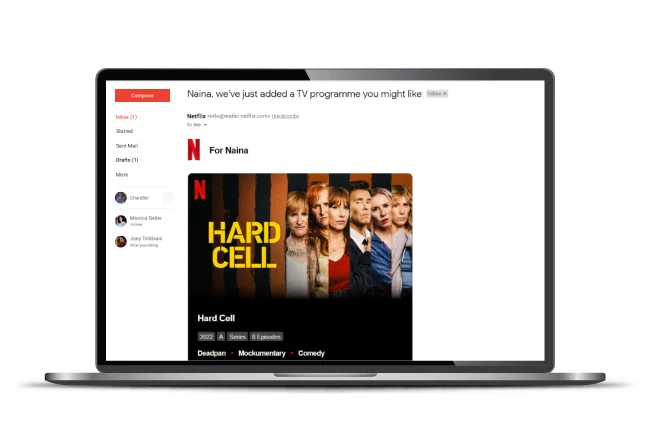
For example, Netflix sends re-engagement emails to its dormant users to send personalized updates on what’s new and what they might like.
5. Discounts for window shoppers
You can create a segment that offers discounts to window shoppers. These users browse a lot, maybe add to the cart, but don’t purchase. Analyze the user’s patterns and set triggers to send well-timed relevant discount offers that engage them at the right time to purchase.
Deploying an AI engine to analyze users’ behavior in real-time and offer discounts at the right time will help here.
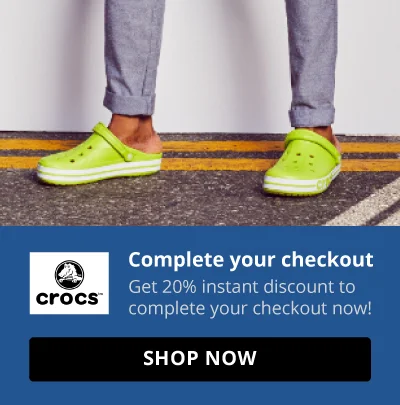
For example, Crocs displays a well-timed web message that offers a discount when the window-shopping user is about to exit the website. This kind of web message can engage window shoppers and encourage them to make the first purchase.
6. Localized campaigns or offers
Use customer segmentation to segment your customers geographically and deliver targeted, localized campaigns and offers. It allows you to localize your unique experience. Geographic segmentation can identify if there has been a recent uptick in the sale of products from a particular region. Use it to your benefit by creating a campaign targeting customers from that region. If you actively track the user’s geolocation, you can change the campaign offerings based on the areas or postal codes they might visit.
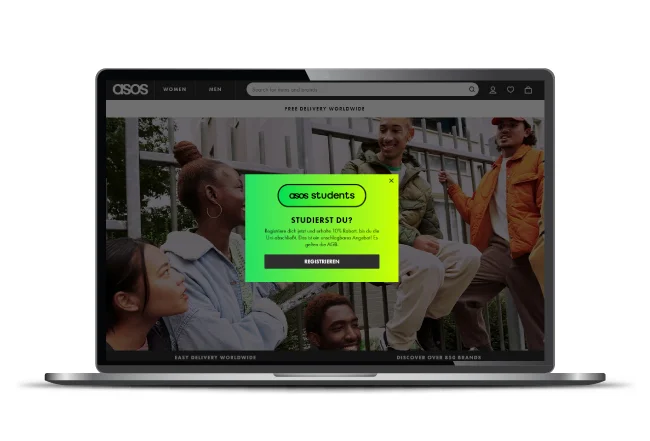
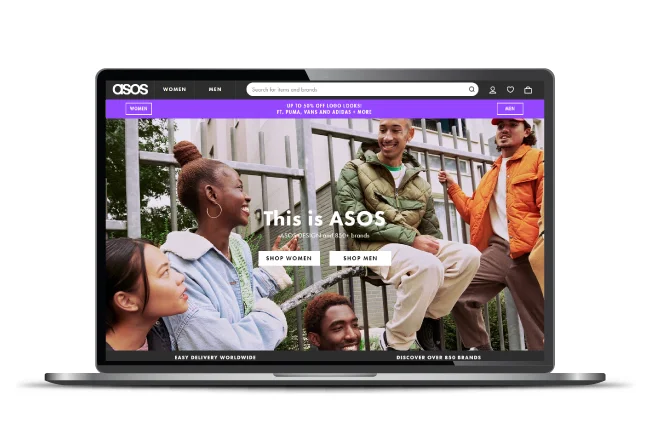
ASOS, for example, automatically selects the appropriate language, currency, experience, and unique offers and promotions for each visitor as its website and all product information is translated into 7 languages and accepts 19 currencies.
What are the benefits of customer segmentation?
Segmenting your customers helps you concentrate your marketing efforts in the right direction, leading to improved customer engagement and loyalty, more sales, and higher ROI. Here are some more benefits of refining a customer segmentation strategy.
1. Deliver a personalized experience
Customer segmentation helps you gain insights into customers’ needs, behavior, interests, values, and more. You can use these insights to deliver a personalized 1:1 experience, including personalized product recommendations, personalized communication, and relevant upsells and cross-sells.
2. Focused marketing efforts and communication
Customer segmentation helps you tailor your marketing efforts and communication to your customer’s specific needs and interests and enables you to maximize the value from each customer. It also allows you to identify the best communication channel for each segment.
3. Generate high-quality leads
The leads generated through customer segmentation are of high quality, and it’s easier to convert these leads into repeat customers.
4. Maximize marketing ROI
With the hyper-targeted customer segmentation approach, your marketing efforts are well-spent on a generalized audience but reach precisely where they are meant to. Marketing budgets are then efficiently utilized.
5. Improve existing products
Knowing your customer segments better allows you to develop and improve your products to align with the new insights. This will help you boost customer loyalty and stand out from the competition.
6. Prioritize customer feedback
Customer insights also include feedback from the customer. You can rank this feedback from the customer depending on the segment that shared it. Inputs from your most loyal customer segments should be addressed first.
Customer segmentation analysis best practices
Here are some best practices to make effective use of your customer segmentation.
Are you looking to increase customer retention, improve conversion rates, or personalize your marketing messages? Clear goals will help streamline your customer segmentation.
Depending on your goals, choose the right segmentation variables, such as demographics, behavioral, psychographic, or a combination of all.
Invest in a data analysis tool that can handle large volumes of data. This tool helps identify patterns, saves time, and provides accurate information.
Customer preferences and behaviors change over time. Regularly review your segmentation analysis and adjust to keep up with customer demands and ensure more relevant targeting.
Create targeted campaigns, personalized messages, and tailored product offerings for each segment. This will help you maximize your marketing ROI and build stronger customer relationships. RFM analysis is another step to understand your current customer behavior and create better segments.
Customer segmentation can become very complex, with many levels and parameters. Starting small and understanding how your segments perform in campaigns can help you understand the steps to take to create more complex segments.
Customer segmentation is not just a marketing exercise. Insights from sales, product development, and customer service teams help create better segments. By following these best practices, you can create an accurate, actionable, and relevant customer segmentation analysis.
Using software for customer segmentation
Here are some examples of what you can achieve with customer segmentation using Netcore Cloud’s customer engagement.
The average user has 80+ apps installed on their phone and uses only 9 or so of them daily. Battling for their attention isn’t easy. Especially if they just opened your app once, viewed something, and forgot about it. Or worse, what if they install your app and forget about it?
Customer segmentation helps target and address precise problems like this and more. Let’s see how to tackle it.
1. Creating the customer segment
Once you have your contact list scrubbed, creating segments is more effective. Continuing from our example, we’ve created a segment that targets users who signed up in the past seven days and launched the app but did not view any content. The problem here is activation.

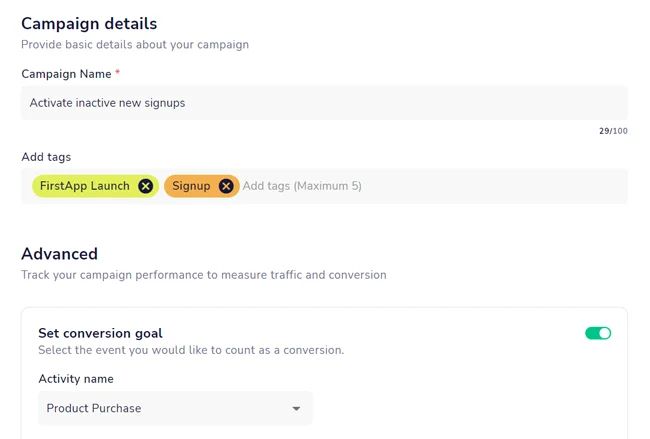
2. Setting up the campaign
If the users aren’t launching your app, you must choose other channels to reach them. Let’s go with SMS since they use the app on their phones. We’re creating a new campaign to get them to purchase a product. The goal can also be a different type of conversion or simply using the app more.
3. Creating content
After selecting the audience (the segment we created earlier, create an SMS or choose from the readily available templates. Here, we’re incentivizing first-time buyers with a 10% discount.
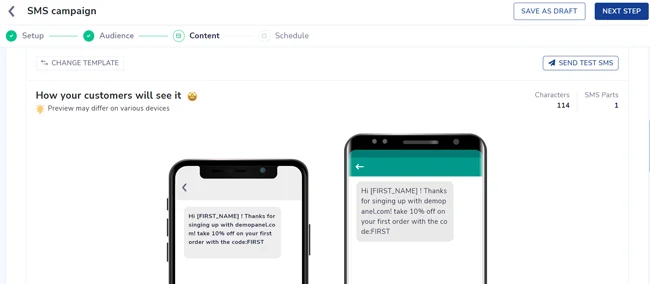
4. Scheduling the campaign
Finally, we schedule the campaign with a start date and time. Then, you choose when to send it to the specified customer segment (new inactive users). The time to send can be ‘now,’ a specified time later, or even better, an optimized send time calculated by our AI engine Raman.
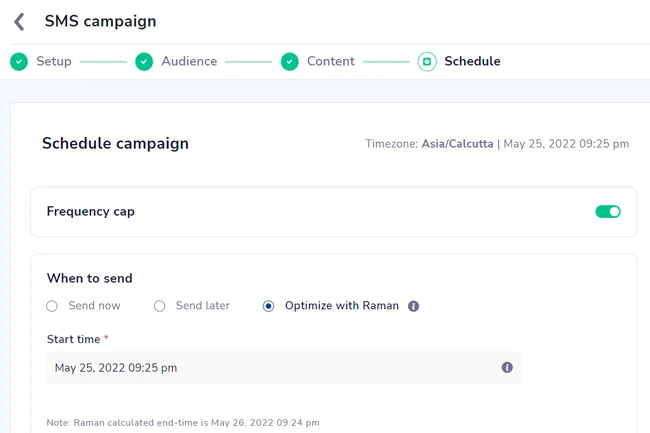
After scheduling, you can preview whether everything is set correctly and publish it. The campaign will start running on your set start date, and your customers will receive an SMS to start their journey with your app.
Role of AI in customer segmentation
Here’s how AI and GenAI are revolutionizing customer segmentation.
Type to create segments and content
GenAI has stirred up the world, and we’re also on board. We have solutions where you, as a marketer, can type a statement, and the tool can generate segments.
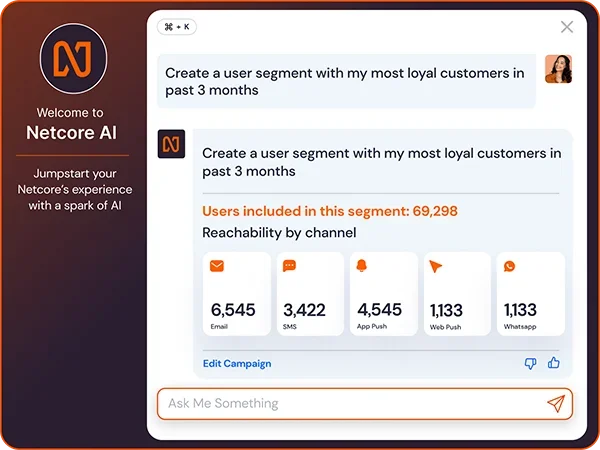
This goes beyond segments, and NLP prompts can also create campaign content:
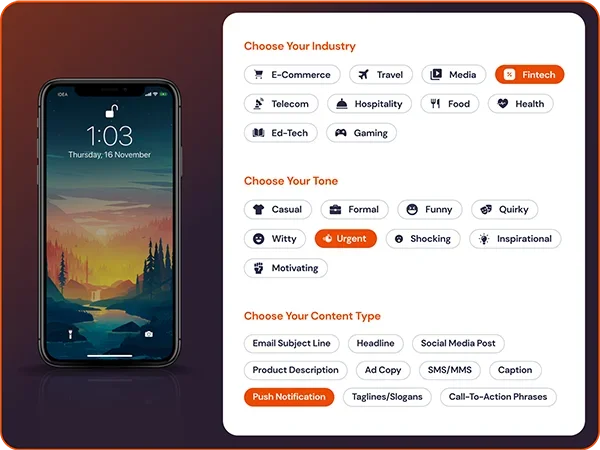
Predictive segments
Solutions like predictive segments analyze historical behavior to help predict whether a user is likely to purchase or churn.
Affinity based segments
AI also helps predict which products customers like. Customer intelligence like this helps run even more targeted campaigns.
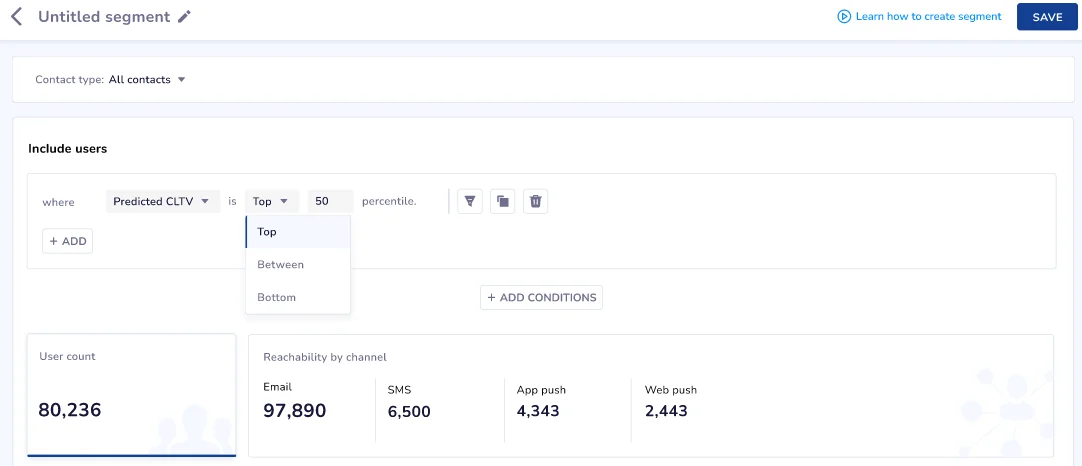
Predict customer lifetime value
With existing data, solutions can also predict a customer’s lifetime value. This helps you identify your potential top and bottom customers and nurture them accordingly.
Conclusion
Customer segmentation organizes your marketing efforts, optimizing your positioning and messaging to meet the needs and expectations of different customer segments precisely. It improves customer engagement and retention and boosts customer loyalty, leading to better budget utilization, improved sales, and higher ROI.
Netcore’s no-code CE platform helps you build a comprehensive customer profile, improve your strategy based on user analytics, personalize real-time website experiences, and orchestrate diverse customer journeys. Learn more about customer segmentation here.