Hackers and stalkers have taken social sharing to a stage where it makes us vulnerable to their attacks. The internet helps them grow faster, learn from each other and makes the act of snooping over someone’s private data easier than earlier. As wise men say – safety is the number one priority. All we can do is to ensure there is a proactive breach-proof technology in place when it comes to transmission of data, and stay ahead of the game.
When we provide multiple levels of assurance, we can improve the user experience along with providing secure communication. We believe that any TLS (Transport Layer Security) is better than no TLS. This is because all certificates, despite their different assurance levels, work to provide session safety and encrypt any data transmitted over the website. Depending on your requirements, we suggest you make a choice that serves your needs best. But first, you need to know what TLS encryption is and what it exactly does, so here you go:
What is TLS Encryption?
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a protocol that implements privacy and data integrity within two communicating entities.TLS encryption is a cryptographic protocol that ensures network security over end-to-end communication. It is the most broadly deployed safety protocol used today by web browsers and other applications that need to privately transfer data over a network. It includes file transfers, VPN links, instant messaging, VOIP and sending messages over email.
TLS is composed of two layers, the TLS Record Protocol and the TLS Handshake Protocol. The Record Protocol renders connection securely. The Handshake Protocol requires the server and client to verify each other first and barter encryption algorithms and cryptographic keys before any data is transferred.
The key features of TLS encryption include-
- Encrypted messages– TLS makes sure that your messages that are sent over emails are secured from hackers. It encrypts the message before sending it so that it is impossible for a third party to interpret it.
- Authentication– This is the process of checking the sender and receiver ID. It is done to verify that the messages are being sent from authenticated sources and the process has no spoofing.
- Standardized websitesTLS encryption is now becoming a standard practice for websites. While Google Chrome is striking out non-HTTPS sites, people are also becoming wary of entering websites that do not have an HTTPS security protocol.
- WidespreadTLS encryption is not limited to only websites and emails, VPN Voice over IPs, and many other such servers who provide end to end communication.
To maximize the utilization of TLS, you should ensure that both the parties have secure SSL/TLS Sessions. Most of the leading ISPs are supporting TLS these days for better transfer of emails.
How does TLS work for an email?
The mechanism and language (protocol) by which one email server sends an email message to another email server is called SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol). For a long time now, email servers have had the choice of using TLS to transparently encrypt the message transmission from one server to the other. TLS used with SMTP, when possible, guarantees that the content of the email is guarded during communication between the servers.
Want to know more on SSL and TLS ?
TLS is initiated with a sequence called TLS handshake. The TLS handshake establishes a cipher suite for communication which specifies the encryption kit that will be shared for that communication. Once this data is encrypted, it is then signed with a Message Authentication Code which can be verified by the recipient to test the authenticity of the data transferred.
The target email server must support TLS for TLS communication to be used. The sending computer or server must be configured to use TLS links when possible.
Here are two examples of emails sent with and without TLS encryption. This will help clarify the meaning and use of encryption:
1. Without TLS encryption
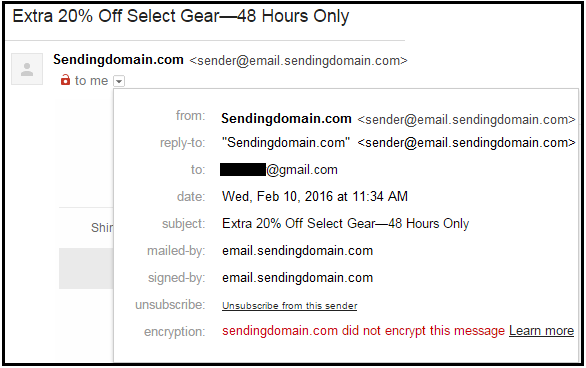
Image 1: Email Without TLS Encryption
2. With encryption
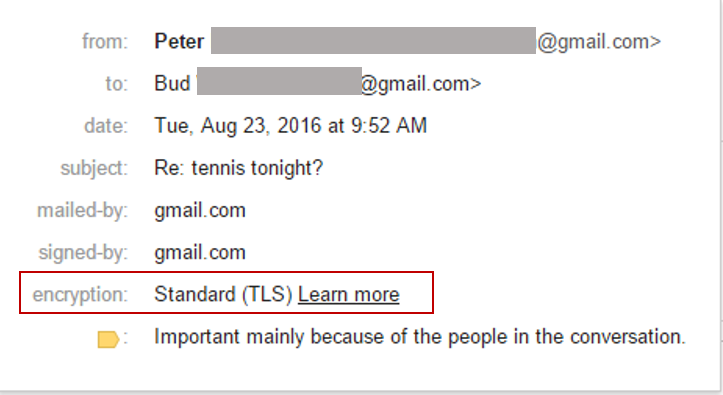
Image 2: Email With TLS Encryption
Image 2 is the perfect example of TLS encrypted email and how the receiver can see it.
Both mail servers are required to support TLS for the encryption process to work. The server and the client recognize which encryption keys to use before anything is broadcasted. The negotiation itself is guarded as well.
Why is TLS important?
When you use a regular POP or IMAP link to download your email (the most common technique in practice), your username and password are carried in clear text over the Internet. This means, that anyone using the same wireless connection, the same channels, picketing traffic at your ISP or anyone in a position to see your Internet traffic can conceivably “hijack” your web traffic and find out your username and password. With this knowledge, they can easily read all your email, steal classified data and/or send out spam emails on your behalf.
TLS encryption shields the transportation of the content in email messages. However, it does not defend the security of the information before it is transmitted or after it reaches its destination. For that, other encryption tools may be used, such as PGP, S/MIME, or storage in a secure portal.
TLS encryption ensures that any information transmitted between the server and client does not fall prey to a man-in-the-middle attack, i.e. spammers attacking the data before it reaches the server. Encryption ensures that data which is being transmitted does not fall prey to attackers.
Opportunistic TLS for Email Security
Are you able to use TLS encryption optimally? If no, then Opportunistic TLS is the solution. To arrive at a clear idea, if the sending server sends an encrypted email but if the receiving server doesn’t accept encrypted messages, then email is sent unencrypted and hence available for email spoofing. Hence, the essential thing is to have an email provider that uses a secure connection. Trusted email service providers (ESPs) like Pepipost have security measures that do not allow unauthorized users from sending messages.
Google’s Email Transparency report can let you find out the statistics of encrypted mail interaction with Gmail Server. The benefits of an opportunistic TLS are a higher sender reputation and 100% spam free delivery.
Failure in TLS Handshakes
The failure rate of TLS handshakes is a topic of concern for system engineers across the world as it causes authentication and security issues. TLS handshakes can be of two types – one based on RSA and other on Diffie-Hellman. These both work on algorithms and if an algorithm fails, it leads to a failure in the TLS handshake. The bottom line is TLS encryption alone is not sufficient to keep your emails secure and authentic.
Considering as a whole, TLS encryption is very important for sending and receiving emails in a secured manner. But, it can fall into some traps and you may suffer a data breach or unsuccessful emails in certain cases. Therefore, it is not a complete solution in case of exceptional situations and you need to handle them on your own.
But, the good news is that there are measures/technologies in place that can alleviate the impact of TLS handshakes. TLS false start is one such program where the server and client can
Special Cases
You might send an email normally without a secondary level of protection. This could be fine if your email is a general email. However, it becomes a matter of concern if you have to send any confidential data over emails. Although most of the popular ISPs support TLS and ensure double protection of your conversations over an email, you cannot ensure the security at the receiver’s end. If the receiver suffers a data breach or hacking at his end, you cannot control your data from being lost or stolen, even though it was secured through TLS encryption.
TLS Vs. SPAM
TLS encryption is assumed to be a secured connection between two ends. It is free from spam most of the time. However, it does not ensure 100% security. There are some companies that have a special kind of spam or anti-virus implemented, which could affect the security of the email message. The whole message may not be encrypted and you may need to ensure the security of the messages while sending them over the internet. Therefore, you must check whether the TLS system is working properly in advance and ensure that there are no loopholes in it.
Also, interestingly you can identify SPAM from Email Headers.
Related Resources
Are SPAM sign-ups bothering you in your online business? Here’s the solution.