The waiter asked me, “Should I get you your favorite wine with the pasta?” as I sat to have an evening meal at my favorite restaurant. Quite impressed by the waiter’s knowledge of my taste, I responded with a nod.
It was cross-selling done amazingly well.
Thinking further about this experience, I realized what happened during that quick interaction was a moment of perfect magical intersection between time, offering, and need. The waiter knew what wine I liked based on my past visits, it went well with the pasta I had ordered, and I, for sure, needed something on the side. All this resulted in a successful cross-selling outcome.
What is Cross-selling?
Cross-selling refers to enticing the customers to buy additional products with items already in the cart. For example, you are buying shoes and the shopkeeper suggests you buy socks. In an online shopping experience think of it like you are buying a camera but you will also get recommendations as soon as you add it to the cart like memory cards, lenses, tripods, green screen, etc. It helps you increase the Average Ticket Size and enhances user experience by suggesting useful add-ons.
Benefits of Cross-selling
Boost Average Order Value (AOV)
Cross-selling based on past customer behavior and buying trends only helps to improve customer experience. According to a McKinsey study, companies that improve customer satisfaction by 20% can achieve a 15–25% increase in cross-sell rates, a 5–10% boost in wallet share, and up to 30% higher engagement.
Improve Customer Experience
Cross-selling based on past customer behavior and buying trends only helps to improve customer experience. According to a McKinsey study, companies that improve customer satisfaction by 20% can achieve a 15–25% increase in cross-sell rates, a 5–10% boost in wallet share, and up to 30% higher engagement.
Retain Customers and Build Brand Loyalty
Building a successful cross-selling strategy helps build brand loyalty and retain customers. A Forbes article highlights that cross-selling can boost customer retention by 75%, underscoring its effectiveness in fostering customer loyalty.
Examples of Cross-selling in Different Industries
Cross-selling strategies vary across industries, but the goal remains the same: encouraging customers to buy complementary or related products. Here are some examples across different industries:
1. Retail & Fashion Industry
- Example: A customer buying a dress is suggested matching shoes, a handbag, and accessories like earrings, and jewelry.
- Why it works: Helps customers complete a look and enhances their shopping experience.
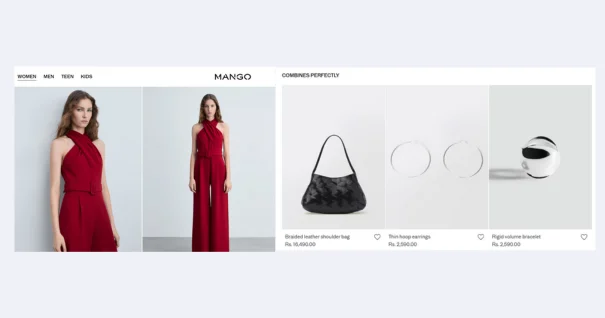
2. Electronics & Technology
- Example: Buying a smartphone? Customers are recommended cases, screen protectors, and wireless earbuds.
- Why it works: Accessories enhance the main product and improve usability.
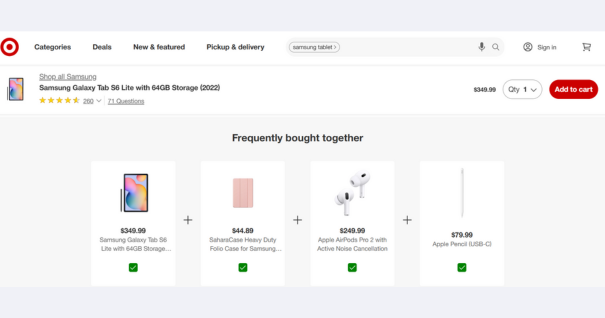
3. Grocery & Food Delivery
- Example: A customer purchasing pasta is shown recommendations for sauce, cheese, and garlic bread.
- Why it works: Encourages customers to buy all ingredients for a complete meal.

4. Health & Wellness
- Example: Someone buying vitamin C supplements is recommended zinc and multivitamins.
- Why it works: Promotes a holistic approach to health and wellness.
5. SaaS & Software
- Example: A company subscribing to CRM software is offered email marketing automation or customer support tools.
- Why it works: Helps businesses streamline operations with integrated solutions.
6. Banking & Financial Services
- Example: A customer opening a savings account is recommended a credit card or investment portfolio services.
- Why it works: Encourages customers to engage with multiple financial products.
7. Fitness & Sports
- Example: Buying running shoes? Customers see recommendations for moisture-wicking socks, a fitness tracker, and energy gels.
- Why it works: Improves performance and customer satisfaction.
8. Home & Furniture
- Example: A customer purchasing a sofa is shown throw pillows, a coffee table, and a rug.
- Why it works: Encourages customers to complete a room setup.
9. Automotive
- Example: Purchasing a car battery? Customers are shown jump starters, battery chargers, and car cleaning kits.
- Why it works: Enhances the vehicle’s maintenance and longevity.
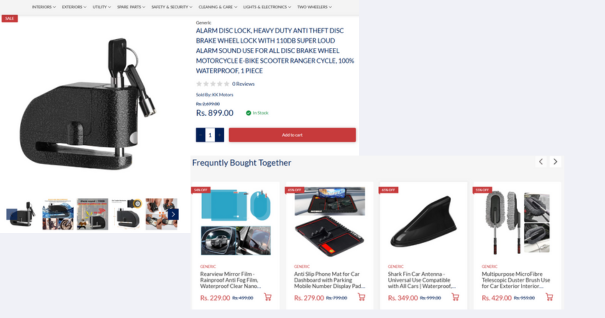
What is Up-selling?
Upselling involves persuading a customer to purchase a more expensive version of a product or to enhance their current purchase by adding more features. For example, in an online shopping scenario like buying cosmetics on Sephora, imagine you’ve added a $270 item to your cart. You then see an offer to buy three of the same items for $550. After a quick calculation, you realize each item would cost you approximately $183, which is more than 50% off the original price. This strategy not only provides customers with a satisfying offer but also boosts the Average Order Value (AOV), leading to increased revenue.
Benefits of Up-selling
Encourage Premium Purchases
Encourage premium purchases by offering a special service for a slightly higher price with a high-end product.
Enhance Customer Experience
Providing customers with extended services, enhanced features, and premium products, along with complementary offers, delivers a compelling customer value proposition.
Increase Revenue and Profit-Margin
Businesses typically see a 10–30% increase in revenue through upselling. You’ve likely experienced this yourself when shopping on Amazon, where you’re encouraged to meet a minimum order value for free delivery or to subscribe to Prime.
Examples of Up-selling in Different Industries
Up-selling strategies vary across industries, but the goal remains the same: encouraging customers to buy high-end or premium products. Here are some examples across different industries:
1. Retail & E-commerce
- Example: A customer browsing online sees a basic laptop priced at $700. A recommendation widget suggests a higher-end model with more RAM and improved processing for $950.
- Why it Works: The customer sees added value in the better features and performance.
2. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Example: Currently on a $20 per month basic plan, the company receives an email from their provider suggesting an upgrade to an enterprise plan for $50 per month, featuring advanced analytics and premium support.
- Why it Works: The business benefits from better features while the provider secures higher recurring revenue.
3. Hospitality & Travel
- Example: A hotel lists a standard room at $150 per night on a booking site, and offers an ocean-view suite upgrade for an additional $50 per night.
- Why it Works: The customer enjoys a better experience, while the hotel increases its profit per booking.
4. Automotive Industry
- Example: A car dealership offers a basic sedan model, but the salesperson encourages an upgraded version with leather seats, a sunroof, and an advanced sound system for an extra $3,000.
- Why it Works: Customers see better comfort and features, making the higher-priced model appealing.
5. Restaurants & Food Services
- Example: A customer orders a regular-sized coffee on the food app, and the app suggests a large size for just $0.50 more.
- Why it Works: Small price increases add up to higher overall revenue.
6. Financial Services & Banking
- Example: A bank offers a standard credit card, but suggests an elite card with cashback rewards, travel benefits, and premium perks for an additional annual fee.
- Why it Works: The customer enjoys extra perks, while the bank earns more through fees and transactions.
7. Healthcare & Wellness
- Example: A gym offers a basic membership, but suggests an all-access pass with personal training sessions and spa services for an extra $30/month.
- Why it Works: Customers see more value in the enhanced experience, leading to higher membership revenue.
8. Telecommunications & Internet Services
- Example: A customer subscribes to a basic 100 Mbps internet plan, and the provider offers a gigabit-speed plan for an extra $20/month.
- Why it Works: Faster speeds appeal to gamers, streamers, and remote workers, increasing subscription revenue.
9. Luxury & Fashion
- Example: A customer buys a $200 handbag, and the store suggests a premium version with designer branding for $350.
- Why it Works: Upselling taps into status-driven purchasing behavior.
10. Online Courses & Education
- Example: A student enrolls in a basic online course, but the platform offers a VIP package with live coaching, certifications, and bonus materials for an additional fee.
- Why it Works: Students want more engagement and personalized learning, leading to higher course sales.
What’s the Difference Between Up-selling and Cross-selling?
Cross-selling is about selling complementary or supporting products along with the main purchase.
Upselling is about convincing your customer to purchase an additional or more expensive product.
| Cross-Sell | Up-Sell |
|---|---|
| – Would you like to have fries or Coke with your meal? | – Would you like to go for a combo meal for $1 extra? |
| – Would you like to buy a set of AirPods with your iPhone? | Would you like to buy an iPhone with double the storage for another $200? |
Finding the Right Moment and Place for Cross-Selling & Upselling
- Help, Don’t Push – Customers aren’t eager for a sales pitch. Instead, focus on genuinely assisting them in their buying journey.
- Timing Matters – Cross-selling and upselling should happen after the customer decides to buy, not at the beginning of their journey.
- Strategic Placement – Position upsells and cross-sells at key locations, such as:
- Shopping cart page
- Near the “Add to Cart” button
- On product comparison or review pages
- Avoid Overcrowding Checkout – Never let cross-sell and upsell offers take center stage during checkout. Instead, introduce them when the customer is ready to pay.
How to Personalize Upselling and Cross-Selling?
Know Your Customers
- Track browsing behavior (pages visited, time spent).
- Analyze conversations with sales or support to identify interests.
- Leverage customer data for better-targeted recommendations.
Use a Dynamic Response Model
- Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, adjust recommendations dynamically.
- Segment customers based on purchase history and spending habits.
- Offer tailored product bundles based on budget size.
Curate Relevant Recommendations
- Provide a balanced number of suggestions (not too many, not too few).
- Ensure recommendations align with customer needs and add genuine value.
- Avoid overwhelming the customer with excessive options.
Make It Financially Reasonable
- Upsells should not exceed a 25% price increase.
- Cross-sells should be at least 60% cheaper than the main product.
- Implement pricing rules for better success rates.
Choose the Right Communication Channel
- Identify preferred customer communication methods (email, SMS, push notifications).
- Test which channels work best for different customer segments.
- Optimize messaging to ensure timely and effective cross-sell/upsell notifications.
Conclusion
Personalization combined with cross-selling and upselling boosts revenue, customer loyalty, and retention. Every additional sale impacts a company’s bottom line, making personalization not just an option—but a necessity. Keep in mind: that your goal is to help customers make better decisions, not just increase sales.
 Worried About Your AI Marketing Strategy? Read the Agentic Marketing 2026 Predictions Report! →
Worried About Your AI Marketing Strategy? Read the Agentic Marketing 2026 Predictions Report! →