How To Send Email In Java Using Gmail SMTP?
Published on 2019-09-18· Updated on 2024-01-25
The author voluntarily contributed this tutorial as a part of Pepipost Write to Contribute program.
Introduction
Sending emails is the most common and necessary requirement for most of the applications. Java provides JavaMail API - a platform and protocol-independent framework to build mail and messaging applications.
The JavaMail reference implementation is licensed under the Common Development and Distribution License (CDDL) v1.1 and GNU General Public License (GPL) v2 with Classpath Exception.
In this tutorial, you will get detailed steps on how to set up JavaMail in your Java project And implement JavaMail API to build and send emails on SMTP protocol.
Prerequisites
- Eclipse IDE
- Java Runtime Environment
Step 1 - Create new Maven Project
- Click onFile > New > Project > Maven > Maven Project

- Select ‘Create a simple project (skip archetype selection)’ and click ‘Finish.
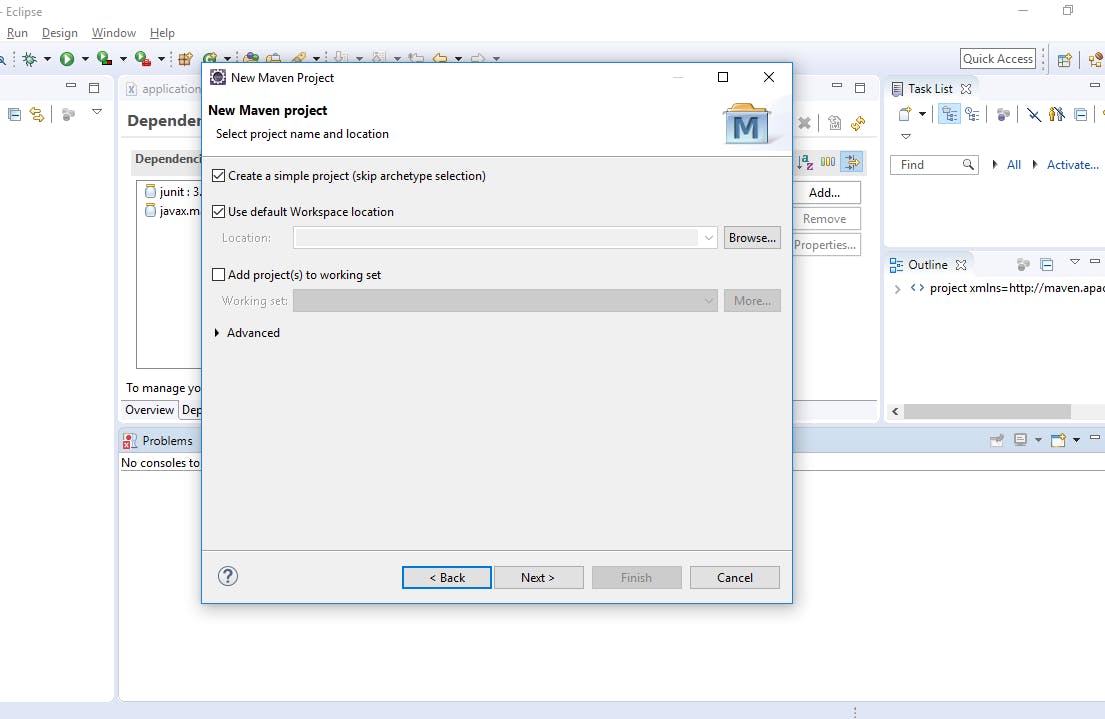
- Give Artifact Id and group Id to your project.

- This will give the default project structure as below:

- A default pom.xml is created:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>SendEmail</groupId> <artifactId>SendEmail</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>SendEmail</name> <description>This artiface will send emails using Java Mail API</description> </project>
- Add following dependencies in your pom.xml file.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.mail</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>This will add javax.mail.jar 1.6.2 into your project resources. You can find the library on the official Oracle website or through Maven.
Final pom.xml:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>SendEmail</groupId>
<artifactId>SendEmail</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SendEmail</name>
<description>This artiface will send emails using Java Mail API</description>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.mail</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.mail</artifactId>
<version>1.6.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>Step 2 - Create Java Class
- Right click on Project and create a new package. Name it com.sendemail

- Right-click on the package to open the context menu.
Select "New" or "Class" (the exact option may vary depending on your IDE).
In the dialog that appears, enter "SendMail" as the class name.
Ensure that the option to create a public static void main(String[] args) method is selected.
Click "Finish" or "OK" to create the class.
Your SendMail class will be generated with the main method, allowing you to write the code for sending emails using the JavaMail API within this class. You can then proceed to implement the email-sending functionality in the main method of the SendMail class.

Import the following packages and classes:
- import java.util.Properties:
This class represents a persistent set of properties. The Properties can be saved to a stream or loaded from a stream. - import javax.mail.Message:
This class models an email message. To send a message,a subclass of Message (e.g. MimeMessage) is instantiated, the attributes and content are filled in, and a message is sent using the Transport.send method. - import javax.mail.MessagingException:
This is the base class for all exceptions thrown by the Messaging classes - import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication:
This class is a repository for a user name and a password. - import javax.mail.Session:
Thisclass represents a mail session. - import javax.mail.Transport:
This is an abstract class that models a message transport. - import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress:
This class represents an internet email address using the syntax of RFC822
Generation of app password
An app password is a 16-digit code that grants permission to a less-secure application or device to access your Google Account. App passwords can only be used when you have 2-Step Verification enabled for your Google Account.
Here's how you can create and use app passwords:
- Go to your Google Account.
- Select the "Security" section.
- Under "Signing in to Google," click on "2-Step Verification."
- At the bottom of the page, find and click on "App passwords."
- Provide a name that helps you remember where you intend to use the app password.
- Click "Generate."
- To use the app password, follow the instructions on your screen. The app password is the 16-character code generated on your device.
- Click "Done."
If you have 2-Step Verification set up but can't find the option to add an app password, it may be due to the following reasons:
- Your Google Account has 2-Step Verification enabled only for security keys.
- You are logged into a work, school, or another organizational account.
- Your Google Account has Advanced Protection enabled.
Tip: Typically, you'll need to enter an app password once for each application or device that requires it.
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage:
This class represents a MIME style email message. It implements the Message abstract class and the MimePart interface.
Sending Email Through Java Using Gmail SMTP
Below is the Java code to send emails using Gmail SMTP server, with the description of each line:
package com.sendemail;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Transport;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
public class SendMail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Recipient's email ID needs to be mentioned.
String to = "[email protected]";
// Sender's email ID needs to be mentioned
String from = "[email protected]";
// Assuming you are sending email from through gmails smtp
String host = "smtp.gmail.com";
// Get system properties
Properties properties = System.getProperties();
// Setup mail server
properties.put("mail.smtp.host", host);
properties.put("mail.smtp.port", "465");
properties.put("mail.smtp.ssl.enable", "true");
properties.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true");
// Get the Session object.// and pass username and password
Session session = Session.getInstance(properties, new javax.mail.Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication("[email protected]", "*******");
}
});
// Used to debug SMTP issues
session.setDebug(true);
try {
// Create a default MimeMessage object.
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(session);
// Set From: header field of the header.
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(from));
// Set To: header field of the header.
message.addRecipient(Message.RecipientType.TO, new InternetAddress(to));
// Set Subject: header field
message.setSubject("This is the Subject Line!");
// Now set the actual message
message.setText("This is actual message");
System.out.println("sending...");
// Send message
Transport.send(message);
System.out.println("Sent message successfully....");
} catch (MessagingException mex) {
mex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}If you want to send HTML content to replace message.setText("This is actual message") with below code:
// Send the actual HTML message.
message.setContent(
"<h1>This is actual message embedded in HTML tags</h1>",
"text/html");Step 3 - Test Java Code
Run a Java application and email will be sent to the recipient. Your console will look like this:

ou have successfully sent email using your Java code.
Now let's send a file attachment in your email.
Optional Steps
Step 4 - Send Email with Attachment.
To send an email with an attachment, you will have to import a few more classes.
1. import java.io.File and import java.io.IOException
The File class is an abstract representation of file and directory path names. The IOException class is a general class of exceptions produced by failed or interrupted I/O operations.
2. import javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart
This class is an implementation of the abstract Multipart class that uses MIME conventions for data.
3. import javax.mail.internet.MimeBodyPart
This class represents a MIME body part.
MimeBodyPart uses the InternetHeaders class to parse and store the headers of that body part.
Below is the java code to send an attachment in the email.
The code has two MIME Body parts, one carrying attachment and other carrying text for email. This is added in Multipart, which is then used to set the content of the message.
Multipart multipart = new MimeMultipart();
MimeBodyPart attachmentPart = new MimeBodyPart();
MimeBodyPart textPart = new MimeBodyPart();
try {
File f =new File("H:\\fakepath\\file1.PNG");
attachmentPart.attachFile(f);
textPart.setText("This is text");
multipart.addBodyPart(textPart);
multipart.addBodyPart(attachmentPart);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
message.setContent(multipart);Here is a running Java code to send attachments in email:
Java Code To Send Attachment In Email
package com.sendemail;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.Multipart;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Transport;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeBodyPart;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart;
public class SendMail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Recipient's email ID needs to be mentioned.
String to = "[email protected]";
// Sender's email ID needs to be mentioned
String from = "[email protected]";
// Assuming you are sending email from through gmails smtp
String host = "smtp.gmail.com";
// Get system properties
Properties properties = System.getProperties();
// Setup mail server
properties.put("mail.smtp.host", host);
properties.put("mail.smtp.port", "465");
properties.put("mail.smtp.ssl.enable", "true");
properties.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true");
// Get the Session object.// and pass
Session session = Session.getInstance(properties, new javax.mail.Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication("[email protected]", "*******");
}
});
//session.setDebug(true);
try {
// Create a default MimeMessage object.
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(session);
// Set From: header field of the header.
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(from));
// Set To: header field of the header.
message.addRecipient(Message.RecipientType.TO, new InternetAddress(to));
// Set Subject: header field
message.setSubject("This is the Subject Line!");
Multipart multipart = new MimeMultipart();
MimeBodyPart attachmentPart = new MimeBodyPart();
MimeBodyPart textPart = new MimeBodyPart();
try {
File f =new File("H:\\pepipost_tutorials\\javaemail1.PNG");
attachmentPart.attachFile(f);
textPart.setText("This is text");
multipart.addBodyPart(textPart);
multipart.addBodyPart(attachmentPart);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
message.setContent(multipart);
System.out.println("sending...");
// Send message
Transport.send(message);
System.out.println("Sent message successfully....");
} catch (MessagingException mex) {
mex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Conclusion
Now you have implemented the Java Mail API successfully and can send emails using any SMTP Server from your project.
We are a community of email enthusiasts. If you have further queries, feel free to drop an email to [email protected], and we would be happy to help you.
Excited about the latest in Bulk Email Marketing! Check out this insightful blog on Gmail and Yahoo updates in the email marketing landscape.
Explore the Blog - Here
Stay ahead of the game with valuable insights on optimizing your email campaigns! 📬
Grade My Email
Check your spam now?
Netcorecloud's toolkit is the solution to all your email problems.

You can also explore
Netcore connects & unifies your data across all sources, connects to your marketing channels and provides you with control over AI Powered automation and personalization.
Deploy emails that are
screenshot worthy!












Rishabh Mishra
Programming Guy! Your coding problem corresponder.